Mastering General and Local Functions in the LCZ4r Package
🗃️ Installation in R
Install LCZ4r in RStudio
To install R package LCZ4r, use the development version on GitHub with latest features

Runing LCZ4r in Posit Cloud
Run LCZ4r directly in Posit Cloud—no RStudio installation required!
🚀 General Functions
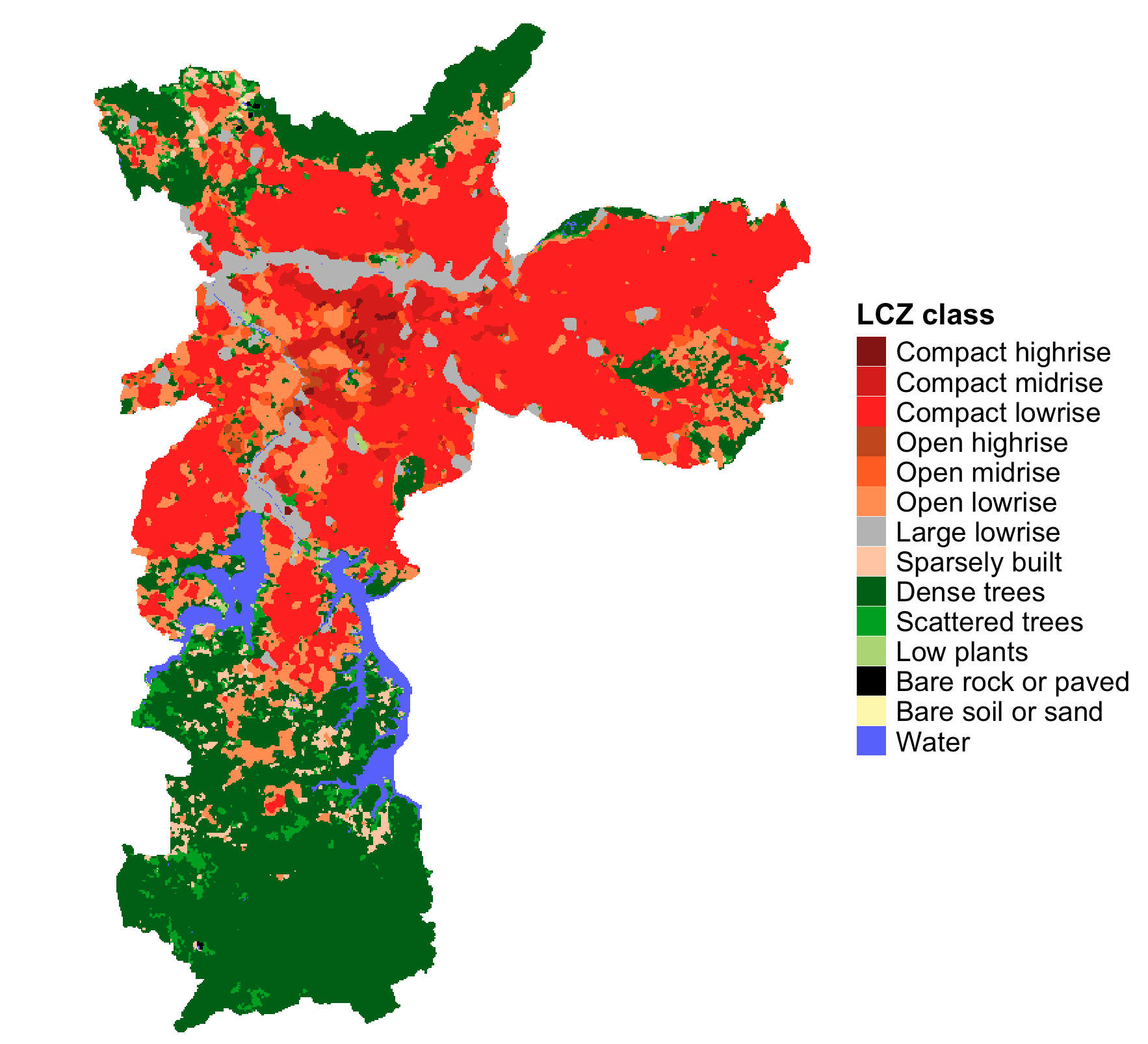
Getting started with General Functions
General Functions facilitate the retrieval, analysis, and visualization of LCZs
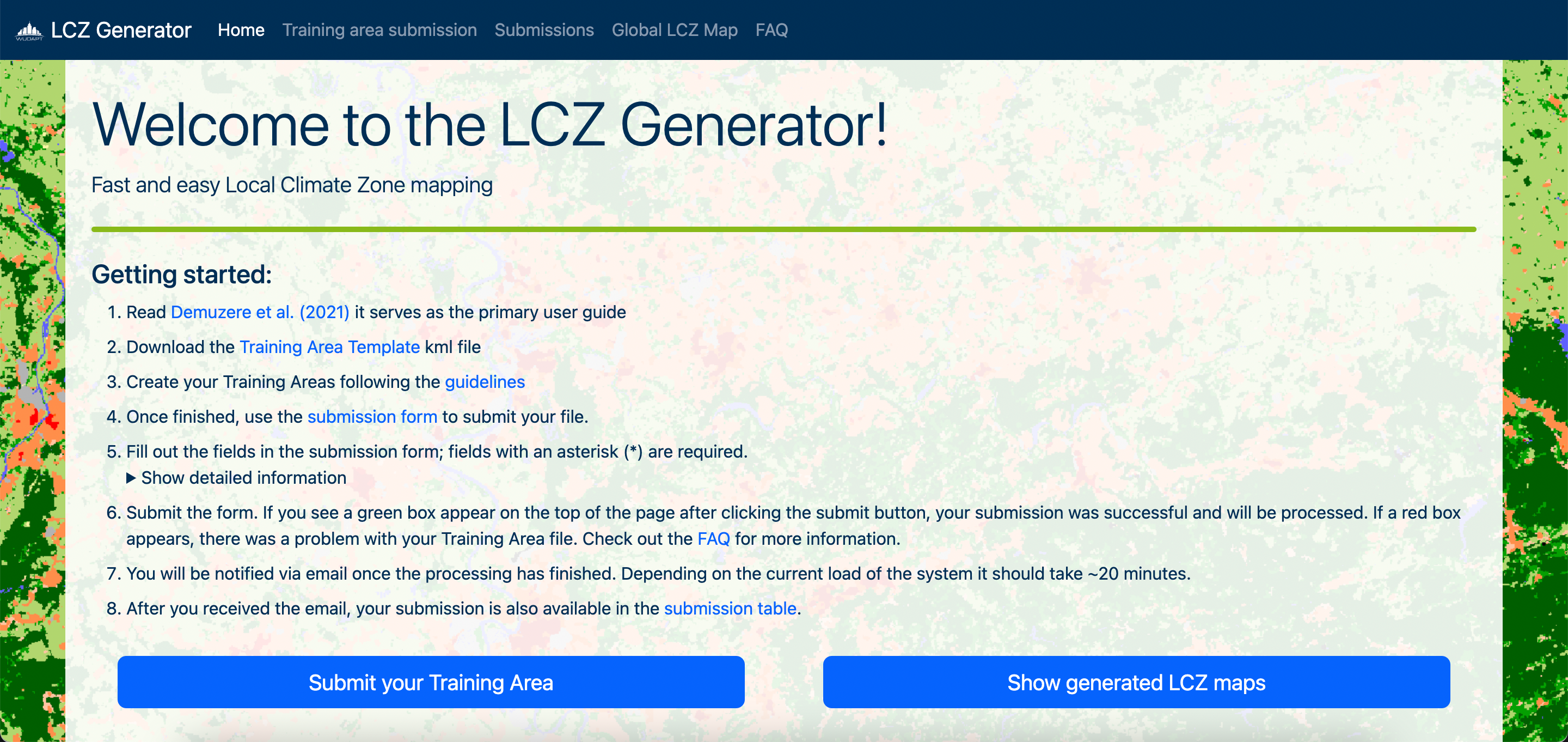
Download LCZ map from LCZ Generator Platform.
The LCZ Generator is a web application for creating Local Climate Zone (LCZ) maps. This guide provides step-by-step instructions to generate an LCZ map for your city using the LCZ4r package.
🚀 Local Functions
Introduction to Local Functions
The Local functions in LCZ4r, offer powerful tools to handle and analyze urban climate data.They enable time-series analysis, mapping of thermal anomalies, spatial interpolation, and more.
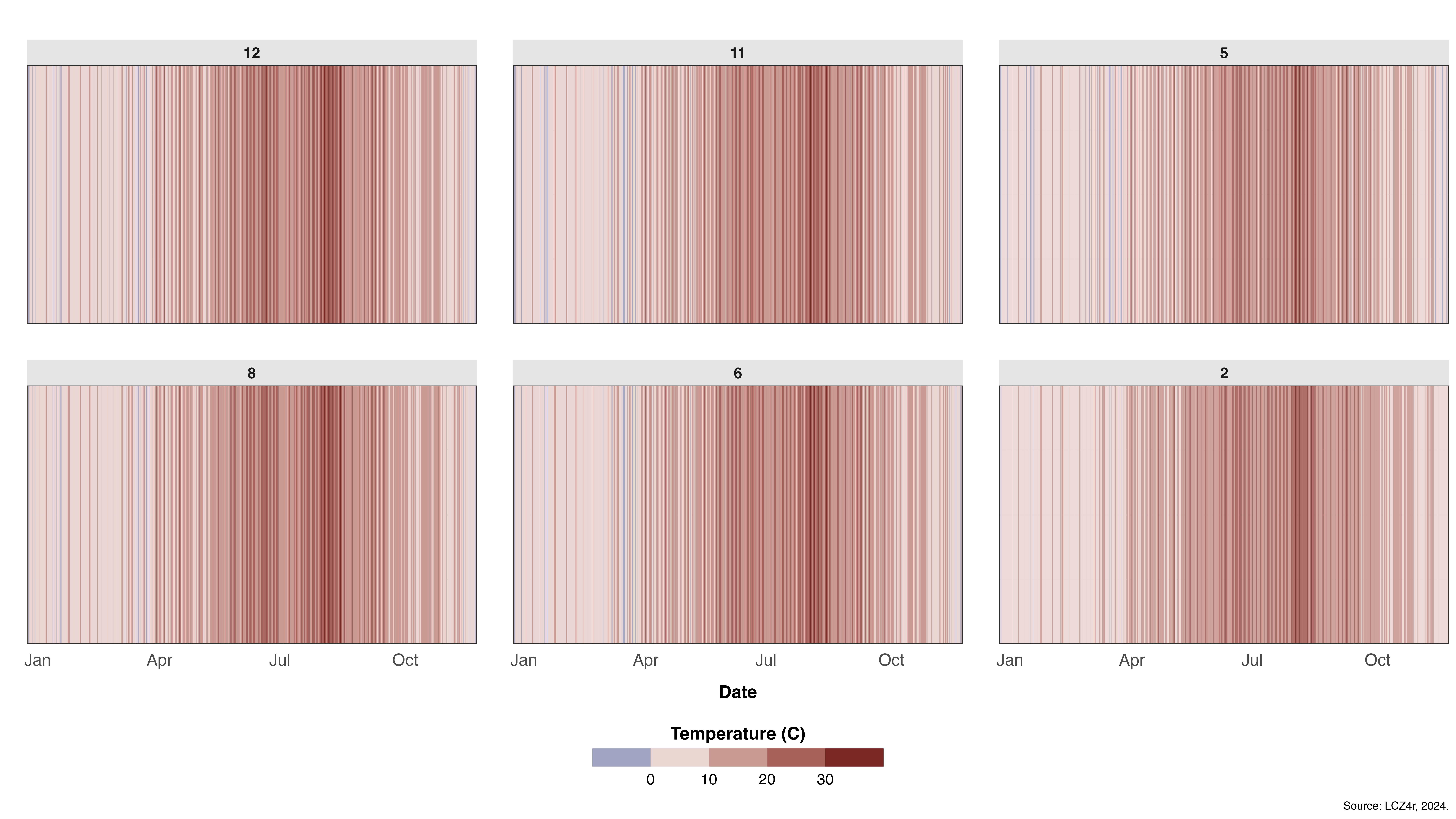
Time Series Analysis
The lcz_ts() function allows you to analyze air temperature data associated with Local Climate Zones (LCZ) over time.
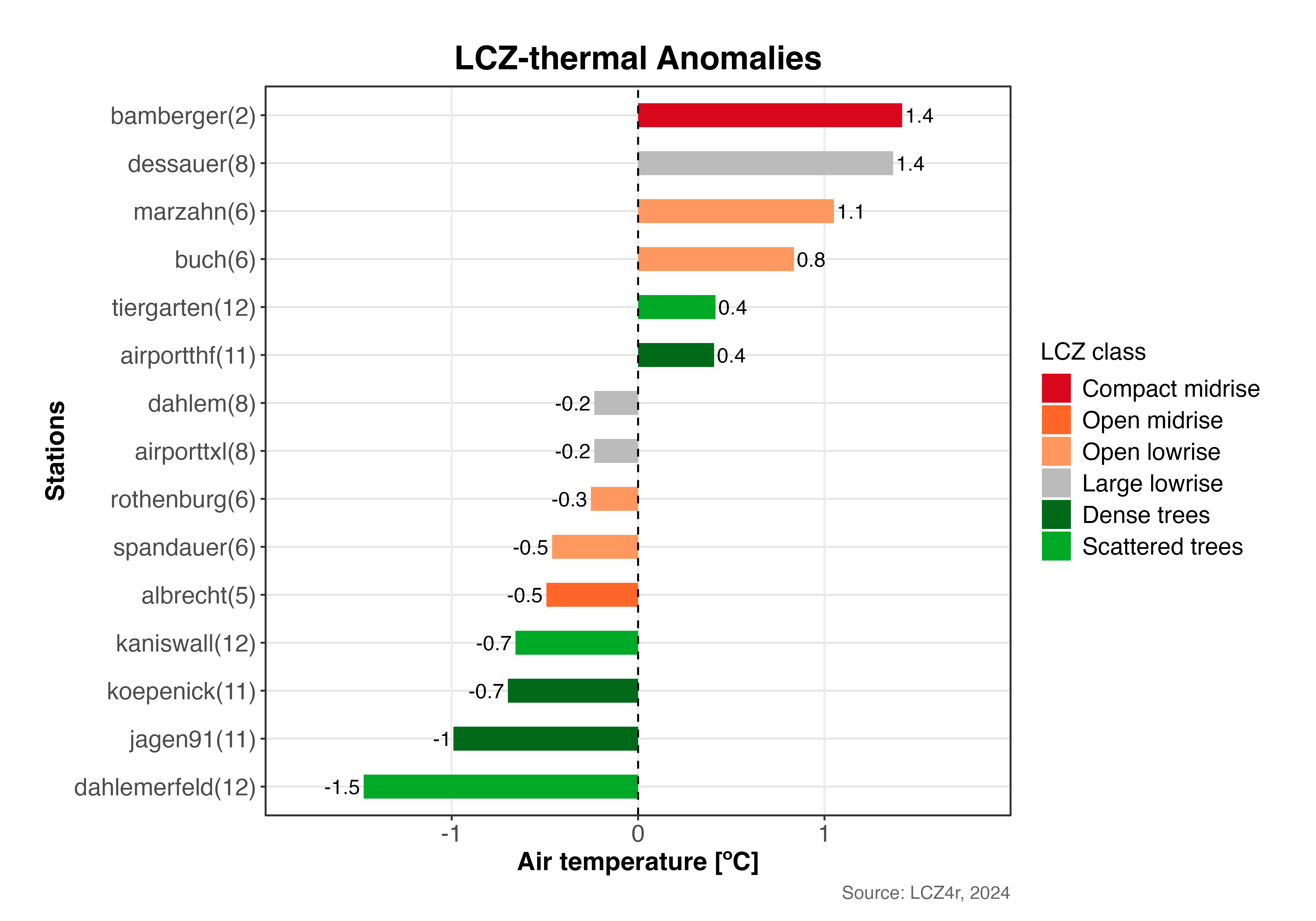
Thermal Anomalies
The thermal anomaly is a great way to evaluate the intra-urban air temperatures differences.
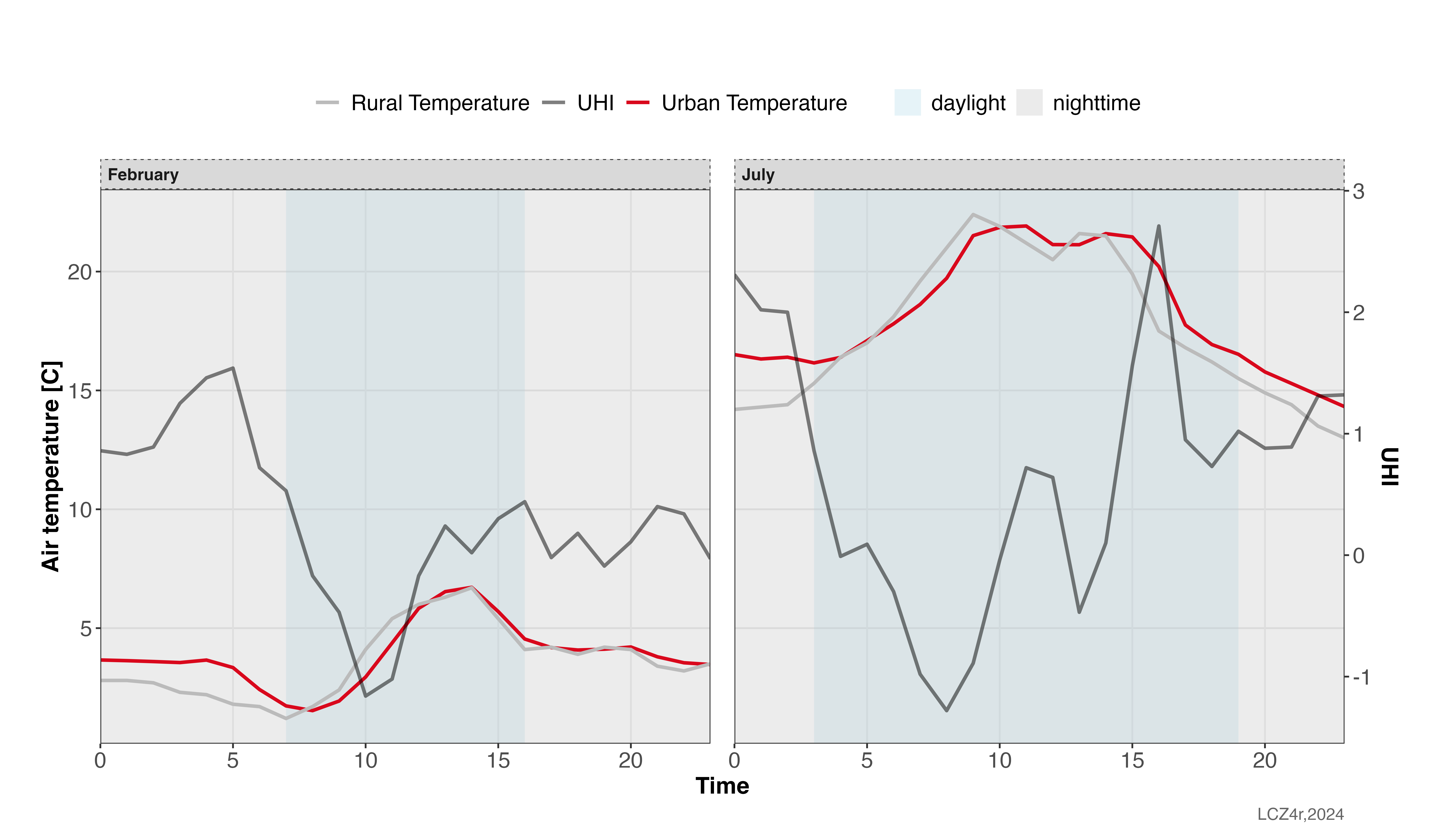
Urban Heat Island (UHI) Analysis
This guide demonstrates how to use the lcz_uhi_intensity() function to calculate and analyze UHI intensity using LCZ classes.
🚀 Modelling air temperature with LCZ4r
Interpolating air temperature and anomalies as LCZ background
In this guide, we’ll introduce how to use LCZ4r to interpolate air temperature and thermal anomalies, using the lcz_interp_map and lcz_anomaly_map funtions
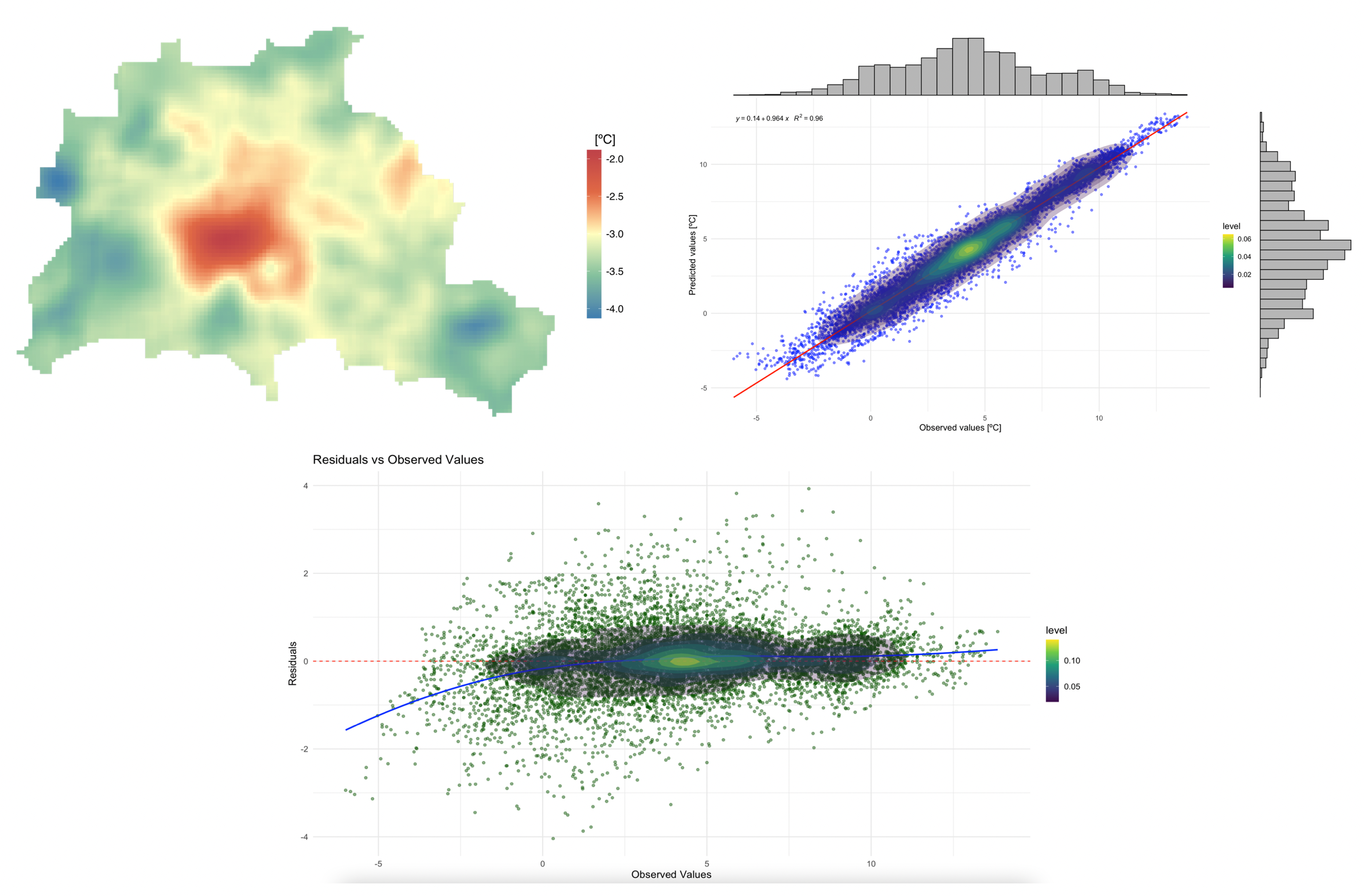
Evaluating LCZ-based interpolation
Here we'll show how to evalute the LCZ-based interpolation for low-density observational data in Berlin

Modelling Urban Heat Island with Crowdsourced air temperatures
In this guide, we'll apply the LCZ4r to model Urban Heat Island with Crowdsourced air temperatures in Berlin